Recently, a research team led by Prof. Jian Liu from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. Ming Hu’s research group from East China Normal University, reported a novel and simple strategy for the synthesis of dual-component Janus nanoreactor with asymmetric structure to realize bifunctional photocatalytic water oxidation/reduction.
Janus nanostructure is a new kind of composite material, which is composed of two or more components with different (usually opposite) physical and chemical properties. Janus nanoparticles possess multiple surface structures that are anisotropic in shape, composition, and surface chemistry, leadingto the different components with unique properties such as surface hydrophilic/hydrophobic, magnetic, optical and electrical properties, etc. Currently, the Janus nanoreactors have been successfully applied in the fields of biomedical, energy storage and conversion, etc. However, it still remains a huge challenge for developing an effective strategy to construct Janus nanoreactors with stable interfacial structure.
This work was published on Advanced Science 2021, 2001987, and is supported by the NSFC,
Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy (DNL) Cooperation Fund, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
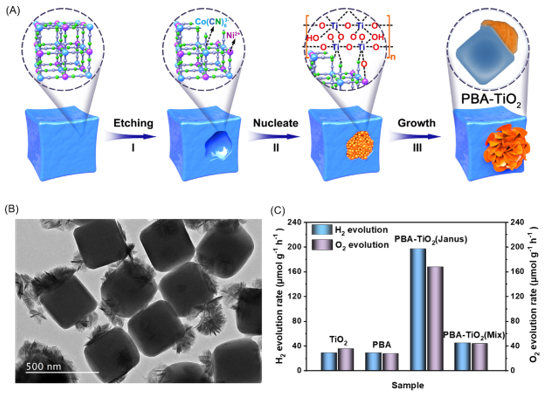
This work presented the rational design and synthesis of the PBA-TiO2 Janus photocatalysts for photocatalytic water splitting. In the synthesis process, the partial dissociation of the PBA cube is induced by mild etching. The unsaturated metal sites on the PBAs can form the chemical bond with the oxygen ions and Ti4+, inducing heterogeneous nucleation of the TiOx on the surface of the PBA single crystals. Then, free-standing flowers assembled by TiO2 nanoflakes are supposed to take root in the PBA single crystals. The PBA-TiO2 Janus nanoreactor gradually emerged and the asymmetric dual-components of nanoreactor possess a synergistic effect due to the presence of the interfacial structure. The forming interfacial structure can promote the fast charge transport and effectively inhibit the photogenerated electron and hole recombination. The photocatalytic activity of PBA-TiO2 Janus nanoreactor for water oxidation/reduction was significantly higher than that of pure TiO2 and PBA catalysts. The etching-regrowth control strategy breaks the limitations of traditional methods on the synthesis of Janus micro/nano structure materials, and provides a new idea for the construction of coordination polymer-semiconductor hybrid Janus micro/nano structure photocatalysts.
http://www.dicp.cas.cn/xwdt/kyjz/202103/t20210305_5969621.html