Our paper entitled with “N-doped carbon spheres impregnated with highly monodispersed ruthenium nanoparticles as a hydrogenation catalyst” has been published online in Chemical Engineering Journal (IF=6.735). Congratulation to Xiaoyan!
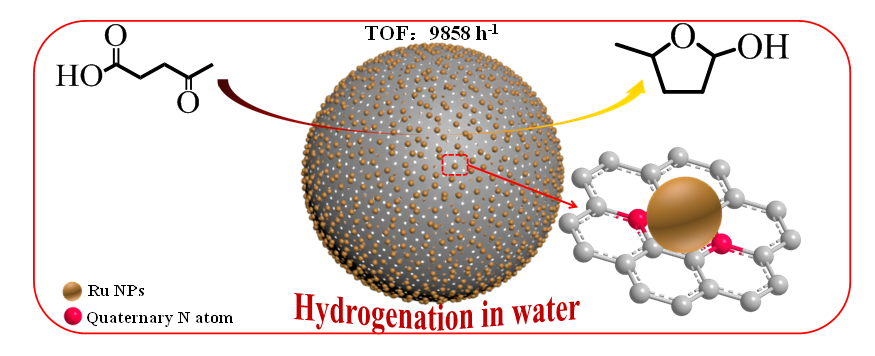
Ru/carbon catalyst has been considered as a very active catalyst in aqueous-phase hydrogenation of bio-resourced carbonyl compounds. High dispersion of Ru NPs on a carbon support could enhance catalytic performance. In this work, well dispersed Ru nanoparticles on the surface of carbon spheres have been developed by the introduction of nitrogen-doping. Compared with carbon spheres without N-doping, the incorporation of the N-dopant with in the carbon matrix effectively improved the dispersion of Ru nanoparticles, which was confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and CO chemisorption characterizations, finding that the presence of quaternary N was responsible for the high dispersion of Ru nanoparticles. Through adjusting the carbonization temperature from 400 to 850 oC, we have shown that the absolute content of quaternary N can be modulated from 3.2 to 22.4 mg g-1. As a result, the dispersion of Ru nanoparticles was improved from 29.8% to 70.9%. The Ru/N-CS-850 catalyst revealed excellent catalytic performance (9858 h-1 turnover frequency) for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone, also demonstrated very high catalytic activity for other hydrogenation reactions.